- When applying Blockchain technology to the procurement / supply chain area, “Inter-company information (including document / transaction) management” seems to be a core area where significant effect is exerted (For the other areas, we may have to doubt the effect). [see the chapter four]
- In Additions, there are some items to be checked when introducing Blockchain. [see the chapter five]
1. Introduction – the purpose of this article
At the regular meetings of Japan Co-buy Network Association (Tokyo, Jan. 2018, Osaka, Mar. 2018), we thought that the next big issue of procurement/supply chain area might be a “Blockchain”. However, at that time, we also did not think that it would be an enthusiastic boom so far.
But today, there is no day not seen the article about “Blockchain”. However, at the same time, there is little information on which procurement professionals can consider its application to their work.
Therefore, for procurement professionals, especially those who are in charge of technology planning and implementation, I described this article with three purposes – 1). Clarifying what the procurement Blockchain is, 2). Clarifying the expected benefits when Blockchain is applied to procurement/supply chain area, 3). Clarifying the checkpoints when introducing procurement/supply chain Blockchain.
2. What is the “Blockchain” ?
Prior to talking about the application to the procurement area, I will begin with what is “Blockchain”. In a word, Blockchain is a mechanism for data accumulation.
For example, “virtual currency” is realized by using the data accumulation mechanism of Blockchain. (Virtual currency is not Blockchain itself).
The major features are the followings;
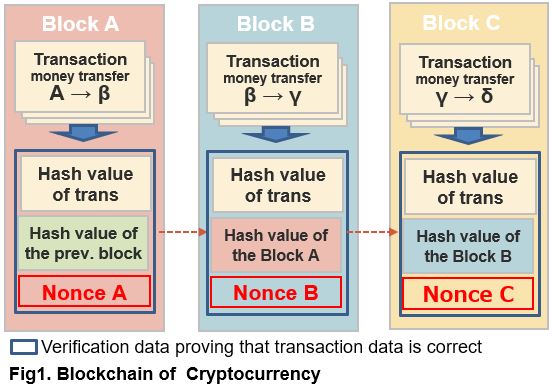
- It deals with a data “block” contains multiple transactions and data to prove the validity of the transaction (blue square of Fig.1)
- The Validation data (blue square of Fig.1) has a hash value (hash calculation result) of the previous block, whereby associates blocks.
- The chained blocks are stored in multiple connected computers.
Because transaction records are stored in distributed “ledger (a book that binds multiple transaction records)” blocks on multiple computers in this way, Blockchain is sometimes referred to as “distributed ledger”.
As described above, “Virtual currency is not Blockchain itself”. However, Blockchain began with the virtual currency “Bitcoin”. Therefore, we will first look at how to use it in virtual currency.
(1) Blockchain in cryptocurrency
Blockchain is a mechanism raised in a thesis “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System (2008)” published by Satoshi Nakamoto, as a technology to realize a virtual currency Bitcoin.
As can be seen from the title of the thesis, in this thesis, the realization of electronic currency (Electronic Cash) was considered. As a result, it showed “electronic currency” apart from the real currency can be realized, if you can fully grasp the records that “who has been delivered from whom”.
(Although it is not true to enter the depth of monetary theory here), the cryptocurrency is like a reward point program (e.g. T point- one of the most widespread program in Japan) that can be transferred. As you know, T points cannot be transferred and is linked with the real currency “Yen” at a fixed rate of 1 point = 1 yen. But what if T points can be transferred between holders?
For example, suppose that there is an initial state record “Only Person α has 10 points (got from the system)”. Here, suppose we have two additional records: “Person α gave 10 points to Person β (when Person α received a candy from Person β)” and “Person β gave 8 points to Person γ (when Person β received a gum from Person γ). Then, when these records are integrated, “Person α has no point, but Person β has 2 points and Person γ has 8 points ” can be clarified.
In this way, when everyone involved can share and refer to all transfer records(who received from whom), they can grasp the current point amount of each other and its legitimacy. Then, the “transferable point” can work equivalent to “money”, that is, it can be used as “cryptocurrency(virtual currency)”.
But for that, there must be a mechanism that can hold transfer records / transaction records without tampering or missing. For that purpose, “Blockchain” is invented.
(2) How the Blockchain works in Bitcoin
In the virtual currency Bitcoin, how is the transaction recorded?
Let’s walk through in order.
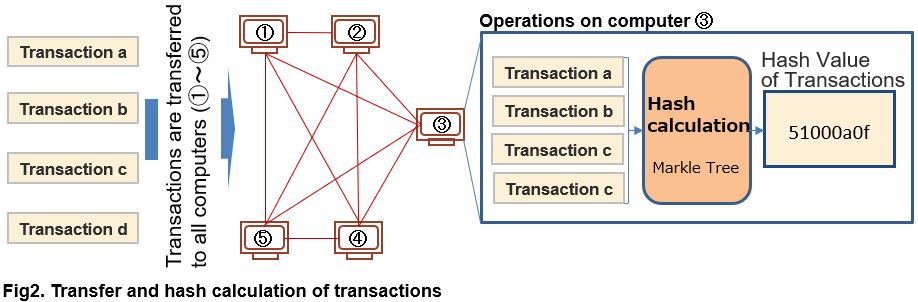
In Bitcoin, when a transaction record “Who sent the bit coin to whom?” occurs, it is transmitted to all computers connected and responsible for creating and storing the block of the transaction record. In this figure it is sent to all of ① ~ ⑤. And all computers begin process to creating a block contains transactions.
(In the figure, the operation is displayed on computer ③, as a representative example of computer ① ~ ⑤).
Each computer first compiles multiple transaction records. Then, calculates the hash value of the transaction record complied. Here the word “hash value” came out. This is calculated using a special function called a hash function. “Special” is that this function calculates different random values when inputs are slightly different and has the nature that it cannot inverse calculate input value from the output.
In other words, it is not possible to estimate the value of the input transaction record from the hash value (output value). The hash value of the output can be known only when calculating inputted transaction record by using the hash function.
As for the hash function program used for calculation, the same thing is provided for all the computers from ① to ⑤ as part of the Bitcoin system. Therefore, if the transaction records to be calculated (input) is the same, the hash value of the transaction records will be the same.
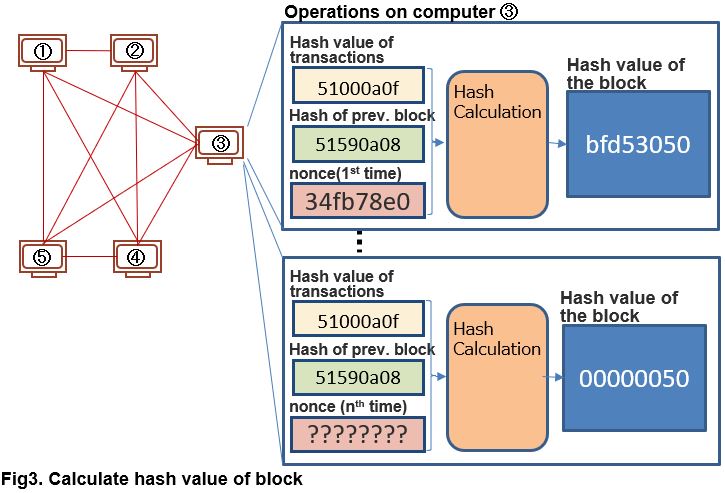
And then, ‘ Competition looking for correct value’ begins among computers.
In Bitcoin, each computer is instructed to find a value (called “nonce”) whose hash calculation result is less than or equal to a specific value (a value having a specified number of leading zero), by using the hash value of the transaction records (“5000a0f” in the figure) and the hash value of the previous block(“1590a08” in the figure). For example, in the above figure, a hash value with 6 leading zeros is requested.
However, as described above, the hash function does not know the output value until calculate it. Therefore, each computer sets a presumed nonce and performs a hash calculation. For example, computer ③ performed a hash calculation first by setting a nonce “34fb78e0”. However, the calculated hash value is “bfd53050”. There is no leading zero, it is an invalid result. This doesn’t make any sense.
However, while calculating the hash value by setting the candidate value of nonce several times, results may match the conditions. In the figure, a hash value satisfying the condition (“00000050”) has come out on computer③ at nth calculation.
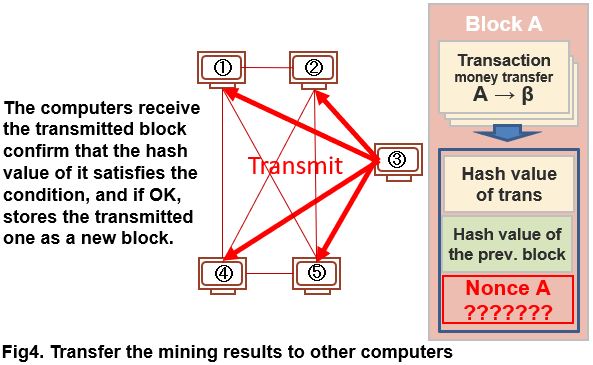
When computer③ has not receive the notice from another computer that has already found the suitable nonce, computer③ sends a block containing the nonce meets the condition to other computers and requests validation of the calculation result.
If the value of nonce is specified, hash value calculation can be done immediately.
Therefore, each computer checks whether the hash value of the block sent by computer ③ satisfies the condition. Then, when confirmed that the result satisfies the condition, each computer stores the block on its own and shifts to the next block creation work.
Then (when a subsequent block is attached to the stored block), computer ③ that found the nonce that satisfies the condition is given Bitcoin as a reward. (Bitcoin system generates the transaction record that Bitcoin as a reward is handed to the computer ③).
This work is referred as “Mining”. As of 2018, when one block is mined, 12.5 Bitcoins (BTC) will be paid as a reward. Currently 1 BTC is about 1 million yen, so you will get 12.5 million yen worth. For Bitcoin, the condition of the number of leading zeros is adjusted as appropriate, so that one new block is created approximately every 10 minutes.
(3) Tamper resistance and autonomy of Bitcoin
Let’s look at Figure 1 again.
In Bitcoin, blocks are linked with hashes of each block , which nonce is discovered accidentally, and it accumulates redundantly on each computer.
Let’s suppose that you tried to illegally rewrite the transaction record of Block A. However, when you rewrite the transaction record, the hash value of the transactions change. Then, to justify rewriting, you must re-do the accidental process again and find a new nonce A. Moreover, the influence is not limited only to the block to be rewritten. Correction in subsequent blocks (B and C) is also required. It requires to search the suitable nonces of subsequent blocks again and rewrite all computer blocks (create new chains). Here is the reason why it could be impossible to tamper with the Blockchain’s transaction record.
In additions, the mining mechanism that gives compensation when finding nonce by mining makes Bitcoin possible to autonomously operate. Participants trying to earn reward, voluntarily take the task of adding new blocks to the chain and it becomes a mechanism whereby operations are permanently continued even if someone does not invest operational funds (If you succeed in mining, you will get a reward of 12.5 BTC (12.5 million yen worth), so everyone will do their best).
As we have seen, Bitcoin is a mechanism only to store transaction records as they are. However, Ethereum, which was developed later, has “Smart Contract” which is a program for processing transaction data. (“Smart Contract” is also inherited to Hyperledger described below.)
after that, in the developed enterprise, “Smart Contract” which is a program for processing transaction data was set up and the mechanism was extended so that processing can be executed before storing the transaction record (this function Are also inherited to the Blockchain business application described later).
*Please note that the virtual currency and the Hyperledger part (describes later) are simplified so that the contents are not too complicated (For example, Number of digits of hash value, transaction-level protection with Encryption keys, etc.).
3. Application of Blockchain Technology to Procurement /Supply Chain Area
(1). When applied to the business domain, mining function was scrapped
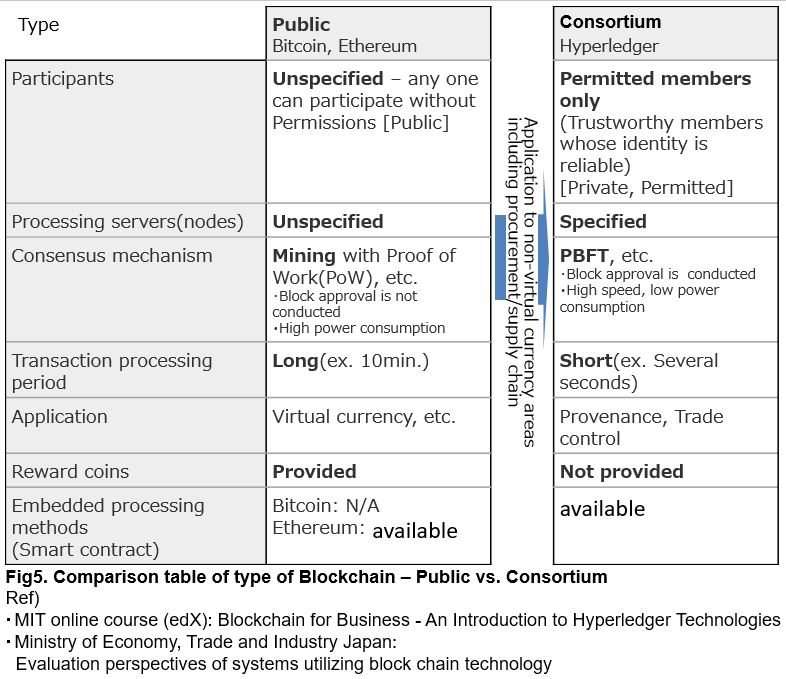
Bitcoin, which started in 2009, withstood various attacks and continues to date. Then, the researches on whether Blockchain (distribution ledger) technology can be applied to other area have begun. Hyperledger is the one of them which describes later.
However, when applied to the business domain, there are things that have been scraped away from the original mechanism of the virtual currency. That is mining.
In virtual currency, mining takes very important role to operate its mechanism autonomously. However, in case of business application such as Hyperledger, which specific participating members pay operating fund, the mining mechanism which consumes huge computing power (electric power) is no longer needed.
Therefore, Blockchain for the business domains (consortium type) was made up, by adopting the mechanism of reliable information accumulation of Blockchain while cutting off its unnecessary portion.
The comparison table is as follows.
(2) Outline of Hyperledger project
The Hyperledger project organized by the Linux Foundation is working to apply Blockchain technology to business (non-virtual currency) domains. This project started in December 2015, just two years ago. In July 2015 (in the almost same period), the beta version of Virtual Currency Ethereum was also announced. Nevertheless, Blockchain has become an enthusiastic buzzword in a brief period. And along with that, various pipe dreams are also coming out. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the current situation correctly and deal with it properly.
The Hyper Leisure Project has the four missions;
- a. create an enterprise grade, open source distributed ledger framework and code base, upon which users can build and run robust, industry-specific applications, platforms and hardware systems to support business transactions.
- create an open source, technical community to benefit the ecosystem of HLP solution providers and users, focused on blockchain and shared ledger use cases that will work across a variety of industry solutions.
- promote participation of leading members of the ecosystem, including developers, service and solution providers and end users.
- host the infrastructure for HLP, establishing a neutral home for community infrastructure, meetings, events and collaborative discussions and providing structure around the business and technical governance of HLP.
(from “Hyperledger Project Charter”)
In other words, the Hyperledger Project is a project that applies Blockchain technology to create open-source foundation on which anyone can build various business systems on it.
And there are the following three frameworks that has already put into practical use or can be expected to be put into practical use shortly. Among them, there is “Hyperledger Iroha” in which Japanese companies are highly involved, as the word “Iroha” indicates.
(3) How Hyperledger (Blockchain for business domain) works?
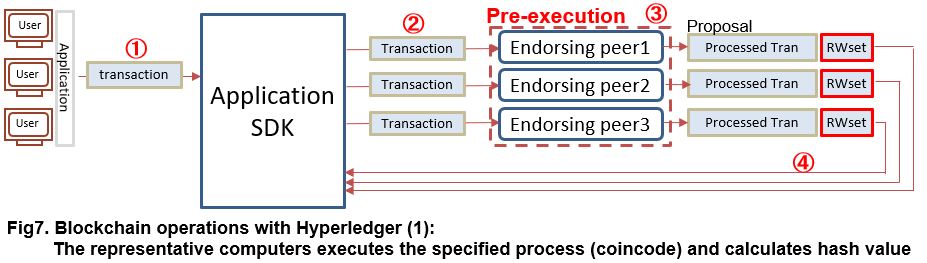
So, how is a transaction executed on Hyperledger? Let’s look at Hyperledger Fabric as an example.
The point is, as mentioned earlier, it is in scraping down the mining function of the virtual currency. Then I will explain the operation along the figure.
① The transaction that the user wants to record is input from the application. Then, the transaction is accepted with “Application SDK”.
② Next, the Application SDK transfers transaction to specific “Endorsing peer” which perform a designate process (Chaincode: so-called Smart Contract of Hyperledger Fabric) on the transaction.
③ Endorsing peer calculates hash value of transaction after preforming “Coincode” process. Then, the calculation result and the hash value of the previous transaction are set in the area “RW set”.
④ Then, in conjunction with the transaction record, return it to the Application SDK.
What is important here are the following two points;
- Searching for matching hash values by varying nonce, such as virtual currency mining, isn’t performed. The hash value is obtained by one-time hash calculation.
- The hash calculation and transaction processing with Chaincode is not done on all peers that store transactions. Only a specific Endorsing peers will do it.
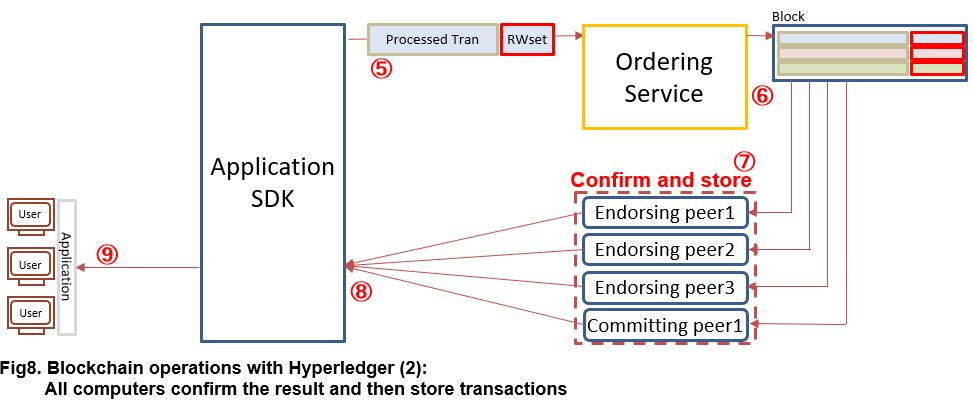
Subsequent processing is to check the validity of the hash value and then store the transaction record in each peer.
⑤ The Application SDK transfer “Processed transaction and RWset data” to “Ordering Service”.
⑥ From Hyperledger Fabric version 1.0, It becomes possible to process multiple transaction in parallel. Unless specified the execution order of the transactions, there was a concern that inconsistent changes will be made in the wrong order. Therefore, Ordering Service is introduced for creating blocks which contains transactions arranged in execution order.
⑦ A Peer which stores the transactions check the contents of the RWset and stores the transaction when the value is correct. In addition, it is possible to have a peer (called a “Committing peer”) that only checks and stores the transaction without executing process③.
⑧ Status information on whether the transaction could be stored normally is sent from each peer to the Application SDK.
⑨ Then, the processing result is reported from the Application SDK to the application. (It is up to the application to handle when an error is reported).
By doing the above processing, Hyperledger Fabric realizes the following advantages;
- Saving the computing power usage and improving processing speed by eliminating searching for hash values by mining.
- Prevent tampering or dropping of data by using the merit of the Blockchain technology
(4) Application examples in procurement / supply chain area
~ (1) Provenonce
In Hyperledger, what kind of application cases are there in the procurement / supply chain area?
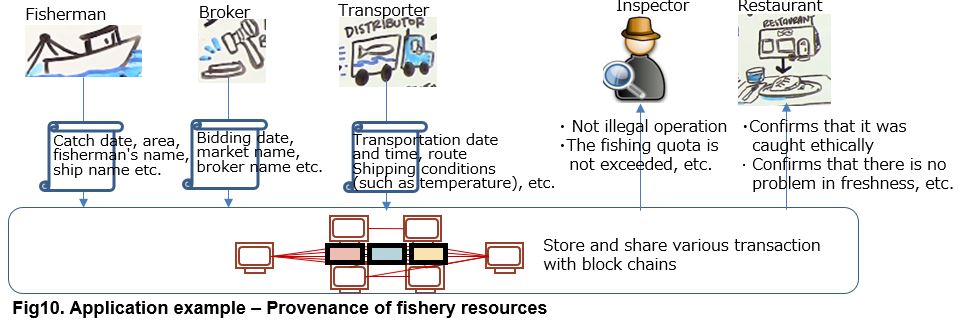
The first is tracking the origin and distribution route of agricultural, forestry and fishery products and minerals.
As a famous example, there is a tracking of fishery resources that became the source of the name of Hyperledger Sawtooth. Below is the overall scope diagram of the trace of fishery resources from introduction video of Hyperledger Sawtooth. By watching the video, you can see the further details.
As shown in Figure 10, Hyperledger Sawtooth uses the Blockchain technology to make up a mechanism, which fishermen and wholesalers can easily register the fish information and then inspectors and restaurant can refer it afterwards.
It is said that 33% of the fish currently being sold is not correctly labeled, and global losses due to illegal fishing operations occur 1 to 2.3 trillion yen annually. This mechanism is expected to be beneficial for improvement of such circumstances.
Besides this, some examples – using as proof that conflict minerals, or displaying certificates of origin on the smartphone screen when customers purchase goods at the Wal-Mart supermarket – has been has been reported recently.
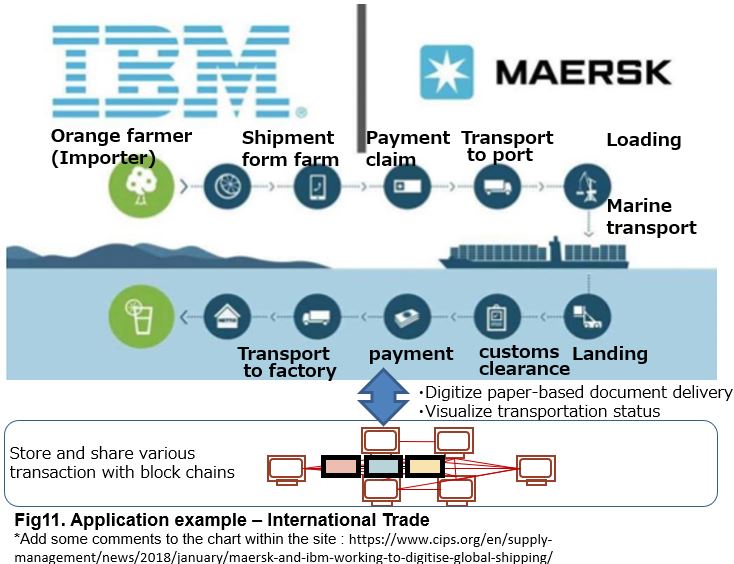
(5) Application examples in procurement /supply chain area
~ (2) International Trade
Another application example concerns the affairs of trade transaction (delivery of documents), which has already been put into practical use. For international trade, various organizations such as port work, custody warehouse, customs, shipping, land transportation, financial institutions and so on are involved. Currently many paper-based documents handlings such as letter of credit (L / C) and bill of lading (B / L) are occurred. Blockchain technology was applied to the such trade transaction handling from the aim of digitizing the delivery of those documents and visualizing the progress of cargo transport. (see commentary video).
This mechanism was put to practical use on Hyperledger Fabric, and practical service began from January 2018 by a joint venture between Maersk and IBM. For further details, you can refer the video (English) and the document (Japanese).
According to the document, cost savings of billions of dollars are estimated only for Maersk related. Furthermore, if we can apply this system globally and reduce “barriers” existing in the international supply chain, global trade volume will increase by about 15% and global effect of increasing GDP by about 5% will be expected (from the estimation by WTO (World Trade Organization)).
In this way, there are not so many, but several actual examples come out in the Procurement / supply chain area.
4. Benefits and Misconceptions of Blockchain Adoption
By the way, in the current very boom of Blockchain, are the items regarded as merit of the Blockchain really appropriate? There are two suspicious things. It is “merit of price side” and “a panacea”. Let’s examine each.
(1) Misconception 1: Blockchain is cheap
It is said, as a big advantage of the Blockchain, that the cost is cheaper than in the conventional system. But is it really so?
a. As to the level of security and availability, the procurement / supply chain area doesn’t require at the same level as financial services which spend a huge budget.
In the financial transaction system handling monetary transactions, tampering or omission of transaction records immediately leads to theft and loss of cash. Furthermore, the financial transaction system has become a social infrastructure that is not allowed to stop for a moment. For this reason, financial institutions spend enormous costs to take thorough and robust security measures on their systems and to maintain full-time operation of them.
However, is it necessary to have such a robust security and availability so far in handling procurement / supply chain transactions? Is there a motivation comparable to financial transactions where falsification instantly leads to cash theft? I doubt it. And if it does not exist, we can reduce the strength of security and save the cost for that.
Regarding availability as well, the level required for the origin certification and trade transactions system is lower than the financial trading system where system downs are not extremely permitted as a social infrastructure. Of course, it is important that the system does not stop frequently. However, when using the cloud service, it will never stop unnecessarily.
Considering like this, there is a high possibility that the cost merit will not increase in the procurement / supply chain systems where the requirement level is lower than financial systems and the cost on them is small.
b. In the financial system as well, the cost merit of Blockchain is not expected to be so large
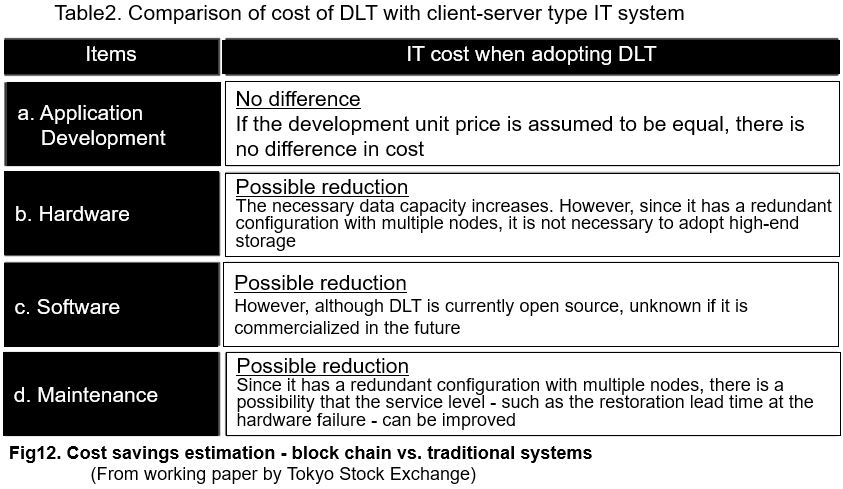
In addition, even in the financial system, there are research findings that the cost merit by application of Blockchain is not so large. In August 2016, the Tokyo Stock Exchange(TSE) issued a working paper titled “Possibility of Distributed ledger Technology for Financial Market Infrastructure“. As to cost reduction, the paper is judged as follows;
The results are as shown in Table 2. An exact calculation is not carried out, but there is a possibility that the cost of hardware / software and the maintenance cost may decrease. However, the cost reduction effect by simply replacing the IT infrastructure is limited, and the main cost impact by adopting the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is brought by improving business process as described in (1).
From these viewpoints, even if the existing system is replaced with Blockchain, it seems that there will not be much cost reduction that is being advertised.
It seems better to pay attention to the sales phrase “Blockchain is cheap”.
(2) Misconception 2: Blockchain is a panacea
Another mistake is that Blockchain are told to be a panacea. For example, when unauthorized modifications of official documents occurred at the Ministry of Finance of Japan, a strong tone emerged to apply Blockchain to public document archiving.
However, as mentioned earlier, we cannot really expect much cost merit, do we really need to bother using the new technology?
As procurement specialists know well, the “contract management module” of the procurement system solution can properly manage the contract document operations (identification of the creator / approver, grasp of the revision history etc.).
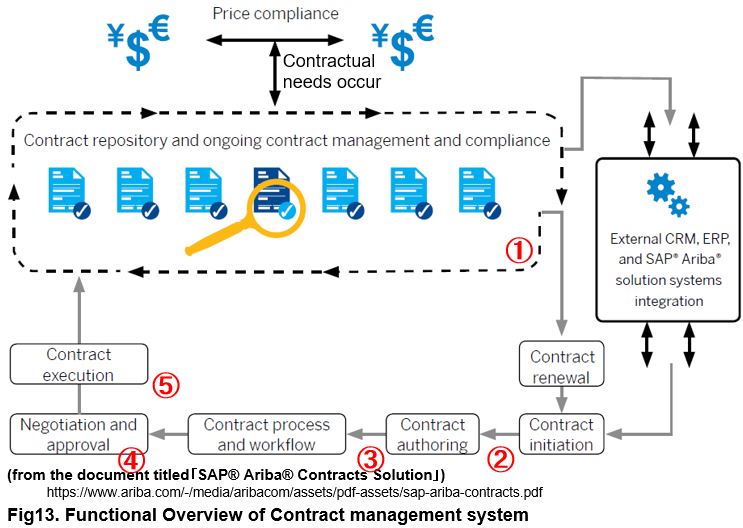
For example, the above figure is a chart of Contract Management in Ariba with my comments added. The contract documents (both “concluded” and “in-process” ) are stored in the repository together with the revision history (the history of where you added or rewritten) (①). To create a contract document, you can input a sentence to a input screen like MS Word and create a draft text. Once the draft text is completed, we will ask the reviewer to confirm the contents (②). As a result, data which keeps the revision history of who checked and who modified it , is recorded in the repository (③). Once the in-house approved draft text is completed, you negotiate it with the negotiating partner. The revision history is similarly accumulated in the repository, and the approval record up to the final approver of the contract is also recorded in the repository (④).
In Japanese companies, the revised contract documents are made on a paper basis, and the reasons for revision are sometimes unclear. However, in Europe and the US where the litigation risk is higher, such a contract management system has already been put to practical use to digitize the contract process and to fully record the revision / approval history.
Of course, the contracts are not just procurement ones. Such a mechanism is also applied to sales contracts. Furthermore, a Japanese pharmaceutical company applies contract management system to the R&D (GxP) document management.
The GxP data is a public document to be submitted to the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan, but the contract management system can adequately manage it. This kind of achievement has already occurred in Japanese companies.
Blockchain is a system with a high communication load, making many exchanges among many computers. In addition, since many computers keep distributed ledger data, central computer does not need to have expensive large processing capacity and high-performance data storage devices. But what if you look at the total amount of data stored in duplicate? With Bitcoin, it is now necessary to have 130 GB of disk space for each computer to store the ledger (this will increase in the future). In that case, the total amount of stored data will be enormous if you think about all the computers. In addition, the TSE’s working paper mentioned above indicates that “application” such as data input screen needs to be customized separately, and its development cost is not much different from the existing mechanism. Furthermore, when developing a new system, it is necessary to take into consideration the occurrence of system bugs (defects).
Considering like this, a so-called “technically withering” mechanism which is already in stable operation without defects may be much safer.
You should be careful about the easy trend of applying Blockchain to anything.
(3) The real advantage – providing a convenient excuse to eliminate inefficiencies among companies
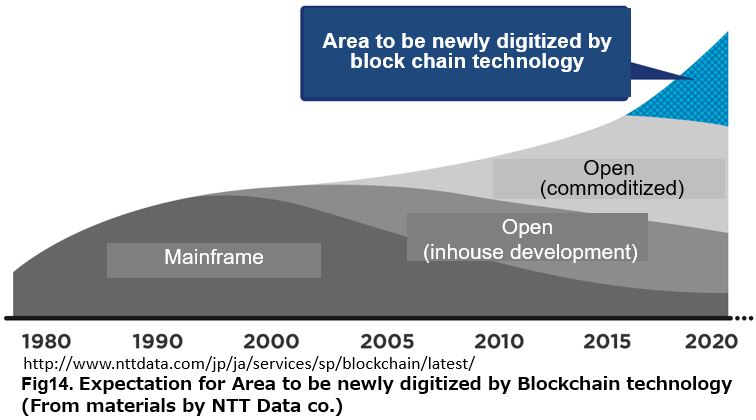
So, what kind of place should Blockchain be applied to? For example, NTT DATA’s report shows the existence of newly effective areas that are currently unsupported. However, because it is considered from a technical point of view, it ends without concretely specifying what area to be applied.
Then, is there such an area? In conclusion, I think that “inter-company document / transaction information exchange” is the area. For example, as mentioned previously, one of the application example is about an international trade. Everyone has already noticed that this area has a huge inefficiency on paper and manual work. However, efficiency improvement and digitization of that area did not proceed. why is it? I think there are two reasons;
- In the circumstance where there are various interested parties, someone did not intentionally take the initiative for improvement. Even if someone can alone create and operate a mechanism for everyone, the merit that he can earn cannot be so great. On the contrary, only complaints will come if it does not go well. In such a place, everybody hesitates to do so-called “volunteer activities”.
- In addition, if the leader appears, there was anxiety about committing your own data there. When delegating data to a person whose intention cannot be truly confirmed, there was anxiety that it might be used disadvantageously.
For the reasons described above, even though there is a great deal of inefficiency, in the area of “inter-company document / transaction information exchange”, it seems that the current situation has been maintained without anyone responding as a leader.
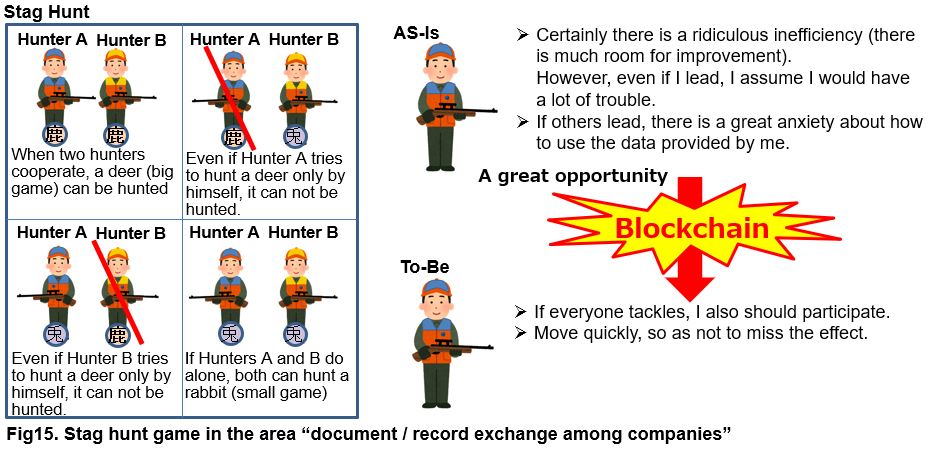
“Document exchange between companies” where “Stag Hunt” game is occurring becomes the main battlefield for procurement Blockchain!
This situation is similar to game theory “stag hunt”. “Stag hunt” is the situation where there are two hunters and two can get a stag (a big game). However, if two choose to do hunting individually, they can get only rabbits (small ones) (but each can definitely get rabbits). Furthermore, if a hunter cannot get the cooperation of another one and try to hunt a stag by himself, he cannot get anything. (Another hunter who chose individual hunting can get a rabbit).
Let’s apply this to “inter-company document / transaction information exchange”. Until now, people who take initiative could not get much benefit, so each has tolerated inefficiencies of paper and manual work. That is, without getting cooperative behavior, each decided that it would be good if a rabbit could be gotten. However, “Blockchain” came in here.
Blockchain is the mechanism that doesn’t need any leader who centrally manages it. The consortium type limited to permitted participants requires an administrator in actuality, but the illusion of the virtual currency obscures such reality. Furthermore, the data is that all participants have the same thing dispersedly and cannot be used exclusively by anyone. If so, the anxiety so far is resolved. Then, “Let’s hurry to jump on the trend so as not to miss it (let’s participate in deer hunting)” … is not it?
In addition, for a digital service vendor, this is a profitable opportunity to provide a new service in the “inter-company document / transaction information exchange” area, which is a white space of service.
In this way, the main battlefield of the use of Blockchain in the procurement / supply chain may become an area of “inter-company document / transaction information exchange”.
The current application cases – provenance and international Trade – are subject to exchange of information among companies/organizations.
Meanwhile, in the area where the control is effective within the organization, it seems that there are already some alternatives other than the Blockchain, and introduction of the mechanism based on the Blockchain will not be rewarded so much.
Also, due to this situation, in the “inter-company document / transaction information exchange” area, the motivation to lead the mechanism becomes poor for the general companies of the participating the Blockchain. (even if a general company takes an initiative, it seems that it can get few rewards correspond to it)
Therefore, I think that service providers such as NTT DATA, IBM, Accenture, or startup companies that find service opportunities would arrange the solution and recruit general company participants in it.
5. Remarks on applying Blockchain
In this way, it is expected that the general company (procurement department) will receive solution proposals from the service vendors and judge them.
Then what is the checkpoints at that time?
The Hyperledger project itself, which leads the application of Blockchain to business area, presents some checkpoints conscientiously.
So, here, I summarized the notes, including technical remarks presented by Hyperledger project at MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) on-line course edX (described later).
Point 1: If the application area is other than “between companies”, sufficient examination is required.
Regarding the application area of Blockchain, as described above, when applying to areas other than inter-company document / transaction information, it is necessary to thoroughly check if there are alternatives that are more effective.
In additions, if you can find “technically withered” alternatives that already in stable operation without defects, they may have far less risk.
In addition, it is necessary to qualify service provider itself and confirm the compliance of the data protection rules of each country.
Point 2: It is necessary to pay attention when data of confidentiality is targeted.
The contents of the transaction record of the Blockchain are basically released to participants (Hyperledger Fabric v1.0 was added the channel function to limit the reference authority). Both the hash value and the encryption key are measures to prevent tampering of contents, and do not limit the reference of contents. Therefore, when you want to store highly confidential information not to be disclosed, you need to be cautious.
For example, personal information such as “My Number (Personal identification number in Japan)” has a big concern to store in the Blockchain.
Point 3: It is not suitable for handling large size data
A Blockchain is a mechanism that sends and receives data between multiple computers(servers) and checks it, distributes it and holds similar data. Therefore, when volume of handling data is too large, it squeezes the communication line capacity, and the amount of data held by each computer can also be enormous. (A technical method of using data link to large-scale data located in another place is also conceivable, but Hyperledger, for example, has not yet realized such method.)
Therefore, if there is a proposal to put data whose data size is too large on the Blockchain, it is necessary to thoroughly examine practicality.
Point 4: It is not suitable for situations where high-speed processing is required
In addition, the mechanism of the Blockchain, which sends, receives and checks data between multiple servers, is of great concern as to whether it can handle tasks that require real-time data processing.
It is not only applicable to scenes that compete for milliseconds such as securities trading transactions, but also we should examine that IoT data processing, which deals with data that many devices send out every time, can be suitable for Blockchain.
Point 5: It is not suitable for tasks where the processing requirements frequently change
The definition of processing program like “Smart Contract” of Ethereum is almost feasible with other Blockchain mechanisms such as Hyperledger.
However, this processing program will be sent to all participating computers in the Blockchain, as well as other transaction information, and handled as special transaction information. Therefore, the duration to complete the setting or change needs as much as processing a normal transaction.
Therefore, it is expected that troubles such as incomplete completion of setting / updating of processing program will occur in case where processing methods change much frequently.
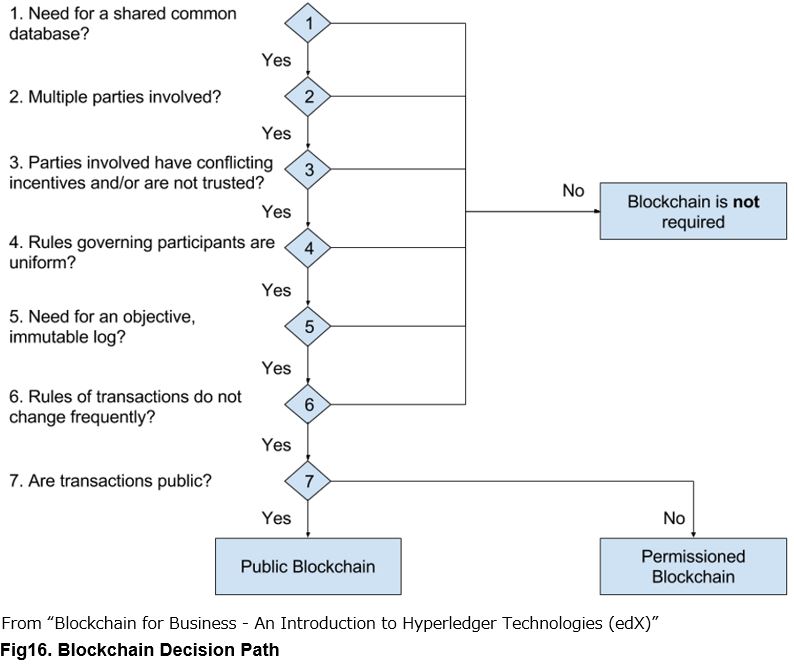
Blockchain Decision Path
As mentioned earlier, the Hyperledger project itself, which is promoting the application of Blockchain to the business domain, has released a chart for judging the suitability of Blockchain. The following is the chart published at MIT’s online course (edX). It seems to be an excellent material for judging the suitability of Blockchain.
6. How to obtain information – Utilizing edX (MIT online course)
The Hyperledger project aiming at business application of Blockchain began only two years ago, in December 2015. However, it is possible to use information directly provided from the Hyperledger Project itself (it is not necessary to wait until it is made into books).
As to Hyperledger, edX (MIT’s online course) gives us the free course titled “Blockchain for Business – An Introduction to Hyperledger Technologies“.
It is expected that rapid innovation will continuously occur, especially in aspects related to technology. In such a case, how to use an effective information source including overseas will become an important differentiator. (Note: Even though information sources are written in English, the accuracy of Google translation has greatly improved.)
*Translated from the original version written in Japanese posted May 3, 2018.